Investigation of nucleosome remodelling by CHD4/NuRD
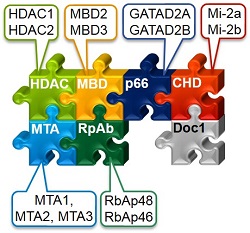 The chromatin-remodelling component of the NuRD complex, CHD4 (or Mi-2), interacts with nucleosomes, but very little is known about its substrates or how it works. Our LC-MS/MS and other studies suggest that CHD4 may interact with nucleosomes having modifications, which may destabilize their structure and play an important role in altering accessibility to CHD4. We are currently comparing the remodelling activity of CHD4 with canonical and non-canonical nucleosomesusing a combination of biochemical remodelling assays and single-molecule FRET.
The chromatin-remodelling component of the NuRD complex, CHD4 (or Mi-2), interacts with nucleosomes, but very little is known about its substrates or how it works. Our LC-MS/MS and other studies suggest that CHD4 may interact with nucleosomes having modifications, which may destabilize their structure and play an important role in altering accessibility to CHD4. We are currently comparing the remodelling activity of CHD4 with canonical and non-canonical nucleosomesusing a combination of biochemical remodelling assays and single-molecule FRET.
In parallel, we are carrying out EM studies to explore whether we can determine the structure of CHD4/NuRD-nucleosome complexes (Zhang et al., 2016).
For further details see:
- Zhang W, Aubert A, Gomez de Segura JM, Karuppasamy M, Basu S, Murthy AS, Diamante A, Drury TA, Balmer J, Cramard J, Watson AA, Lando D, Lee SF, Palayret M, Kloet SL, Smits AH, Deery MJ, Vermeulen M, Hendrich B, Klenerman D, Schaffitzel C, Berger I, Laue ED. The Nucleosome Remodeling and Deacetylase Complex NuRD is built from preformed catalytically active sub-modules. Journal of Molecular Biology, 428(14): 2931-42 (2016), PMID:27117189
Members of our group currently involved in this project are:
Jenny Balmer and Wei Zhang
